Baldness in dogs, causes
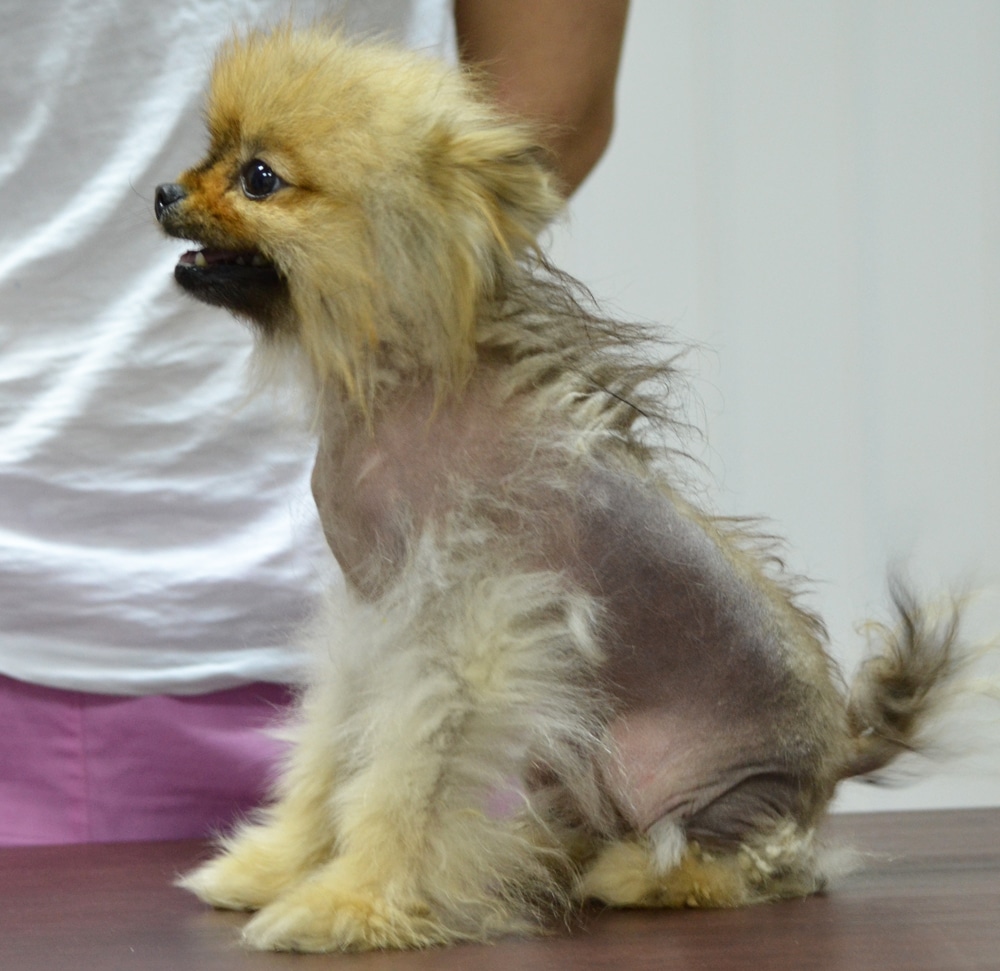
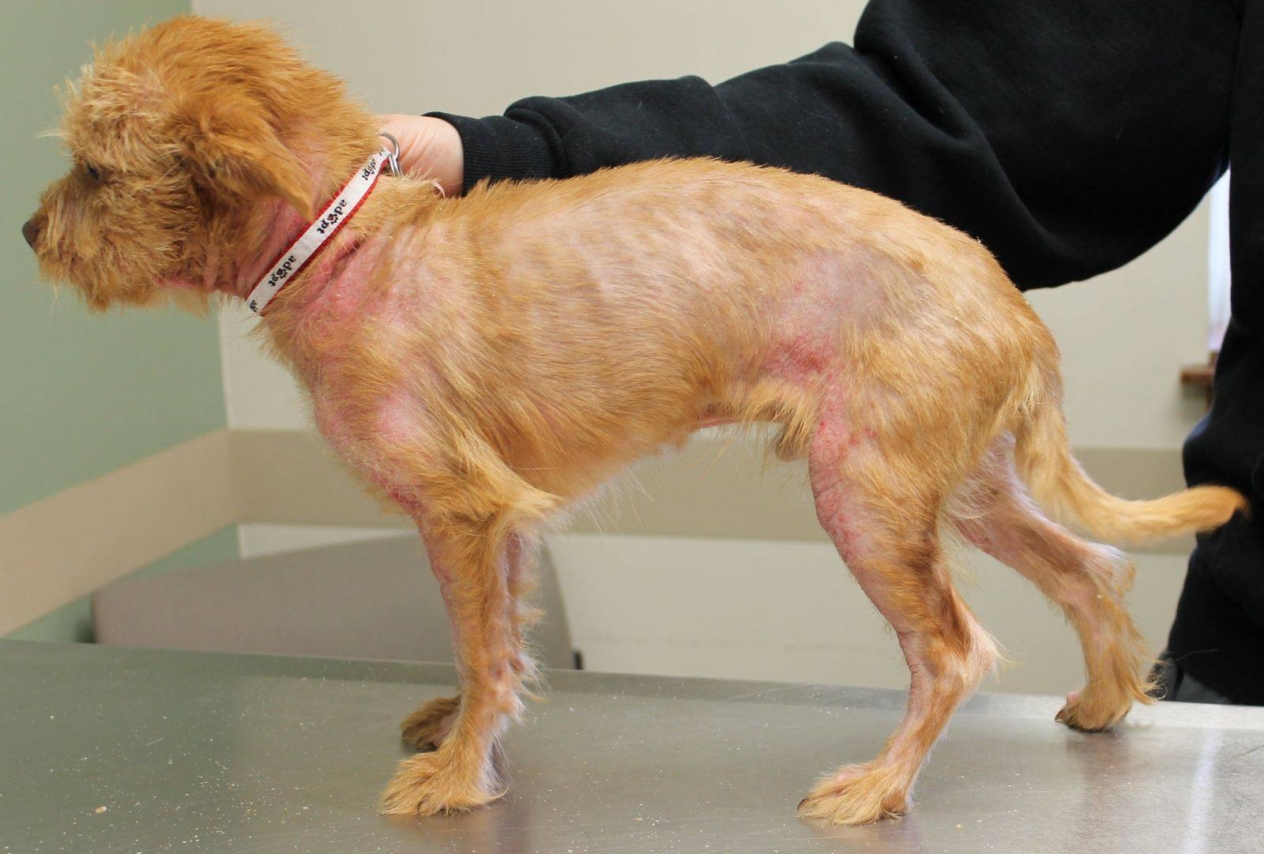
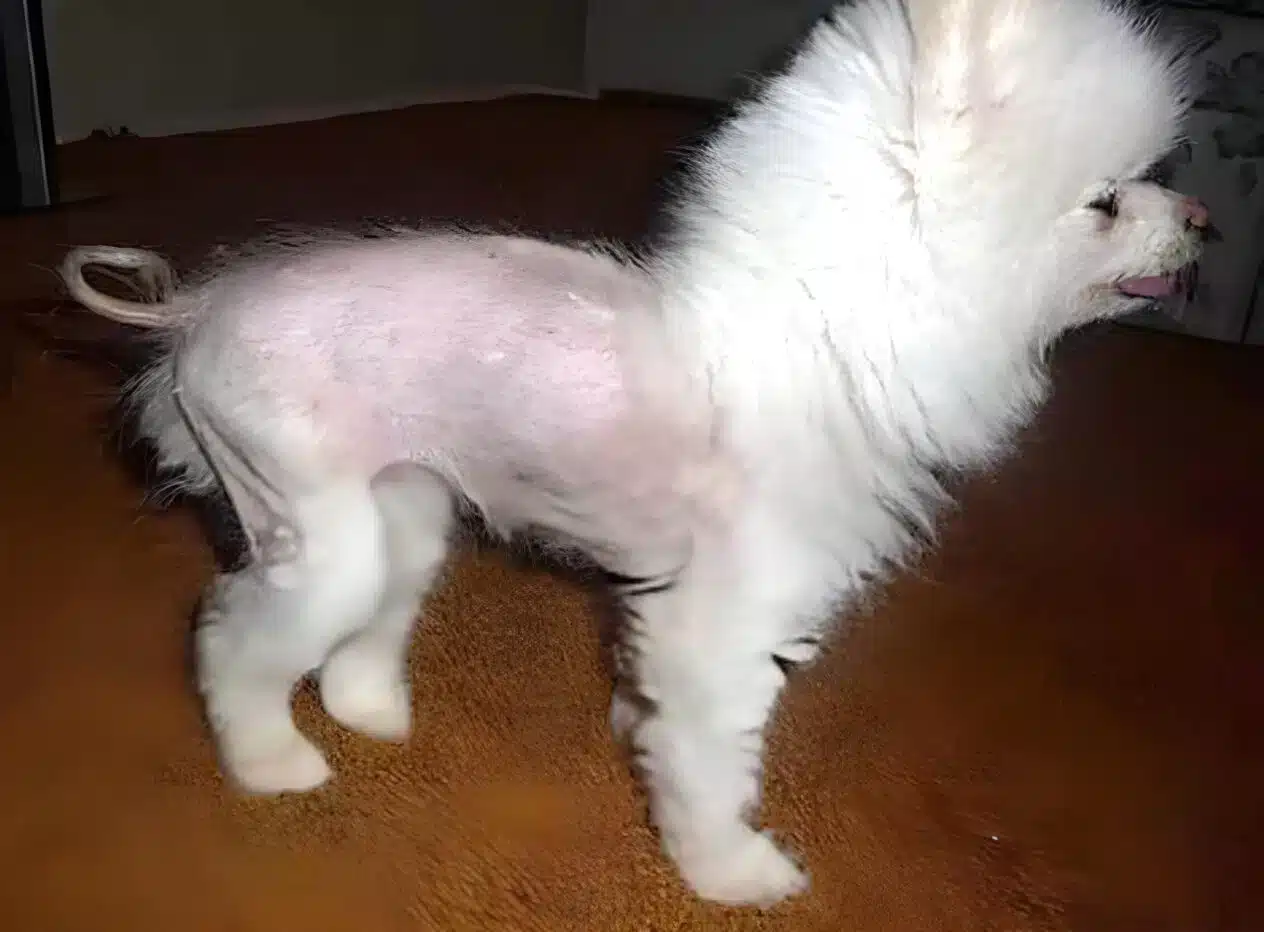
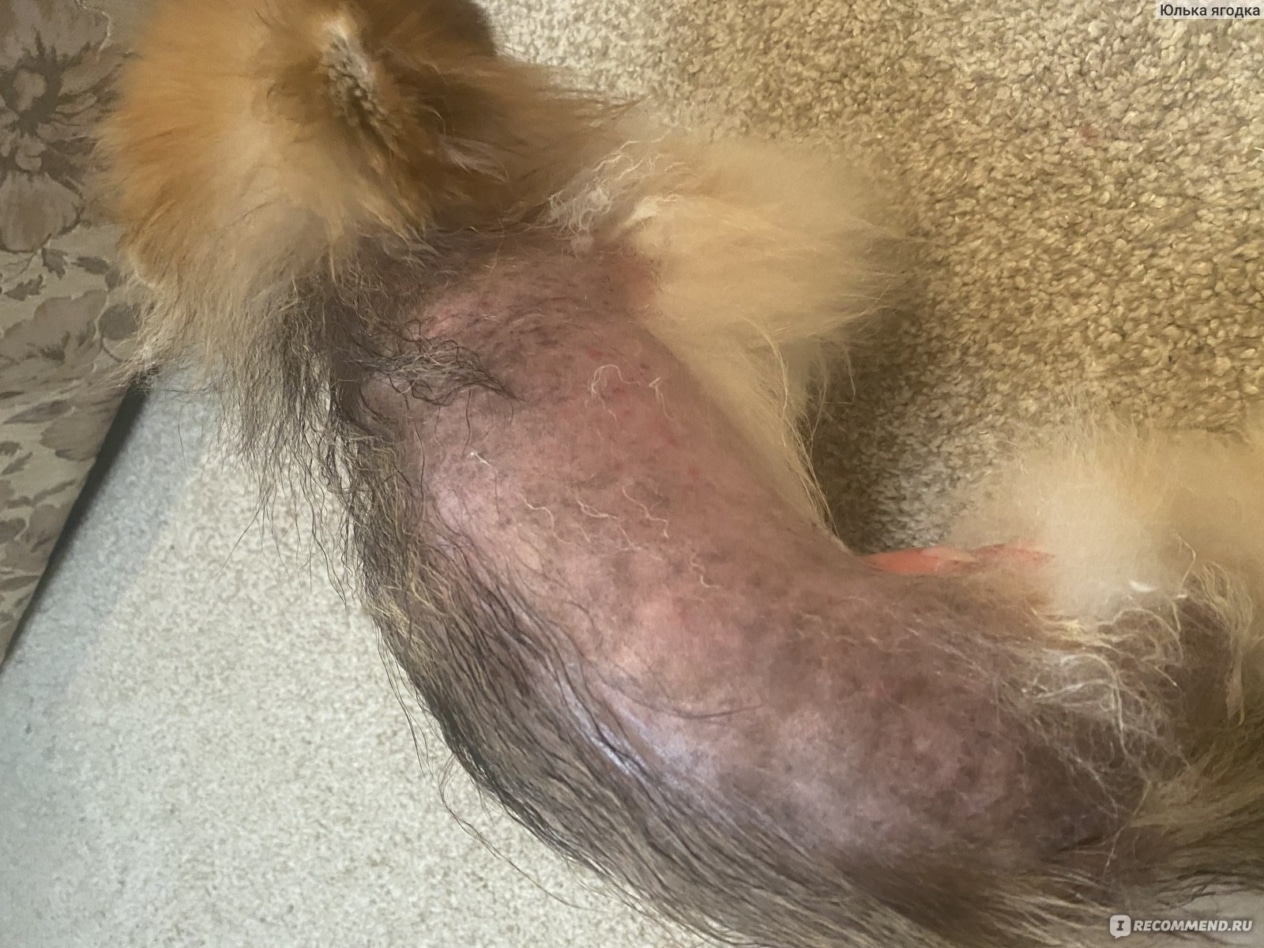

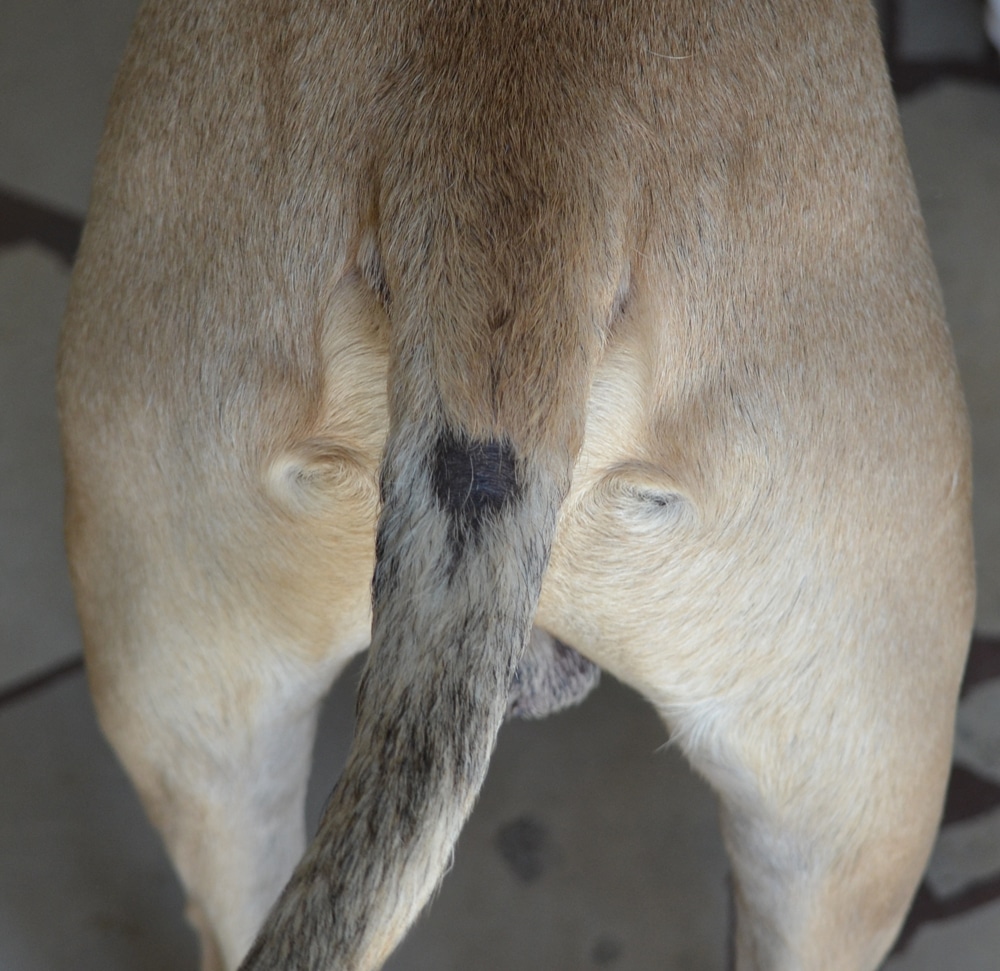
Alopecia in dogs, or hair loss, is a fairly common problem that can be caused by a variety of factors, from allergies to hormonal disorders. Understanding the causes of alopecia areata, its symptoms and treatments are important for pet owners who want to ensure the health and comfort of their pets.
The causes of alopecia in dogs can be diverse and include the following factors:
Allergies: Allergic reactions to food, flea bites, pollen or other irritants can cause itching, skin irritation and coat loss. Usually, in such cases, hair falls out in places of severe itching, because the dog can scratch or gnaw the affected area.
Infections and Parasites: Bacterial or fungal infections, as well as the presence of parasites such as fleas, ticks or hair-eaters, can lead to shedding. Usually, such conditions are accompanied by itching, redness or peeling of the skin.
Hormonal disorders: An imbalance of hormones, such as thyroid hormones (hypothyroidism), cortisol (Cushing’s syndrome), or sex hormones, can cause alopecia. This type of hair loss is usually symmetrical and is not accompanied by itching.
Autoimmune diseases: Some autoimmune diseases, such as lupus or vitiligo, can affect the skin and cause alopecia.
Genetic factors: Some breeds are prone to alopecia due to hereditary factors. For example, the Chinese Crested Dog or the American Hairless Terrier have a tendency to lose their fur.
Stress and behavioral factors: Prolonged stress or behavioral disorders can lead to excessive licking or biting, which can also cause alopecia.
As you can see, the causes of baldness in dogs can be as diverse as possible, so the groomers from our beauty salons for dogs advise first of all to pay attention to the manifestation of symptoms, which we offer to read in more detail below.

Symptoms of alopecia in dogs
Alopecia symptoms can vary depending on the cause, but the main manifestations include:
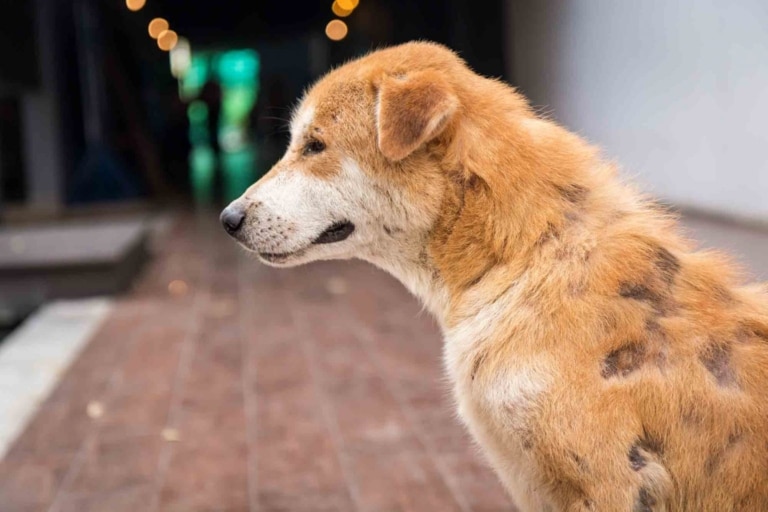
– Hair loss: Focal baldness in dogs or complete loss of hair on different parts of the body.
– Peeling or inflammation of the skin: The skin may appear red, dry or scaly.
– Itching or irritation: The dog may actively scratch or bite the affected areas.
– Change in skin color: At the place of hair loss, the skin may be darker or lighter.
– Skin lesions: Ulcers, blisters or crusts may appear.
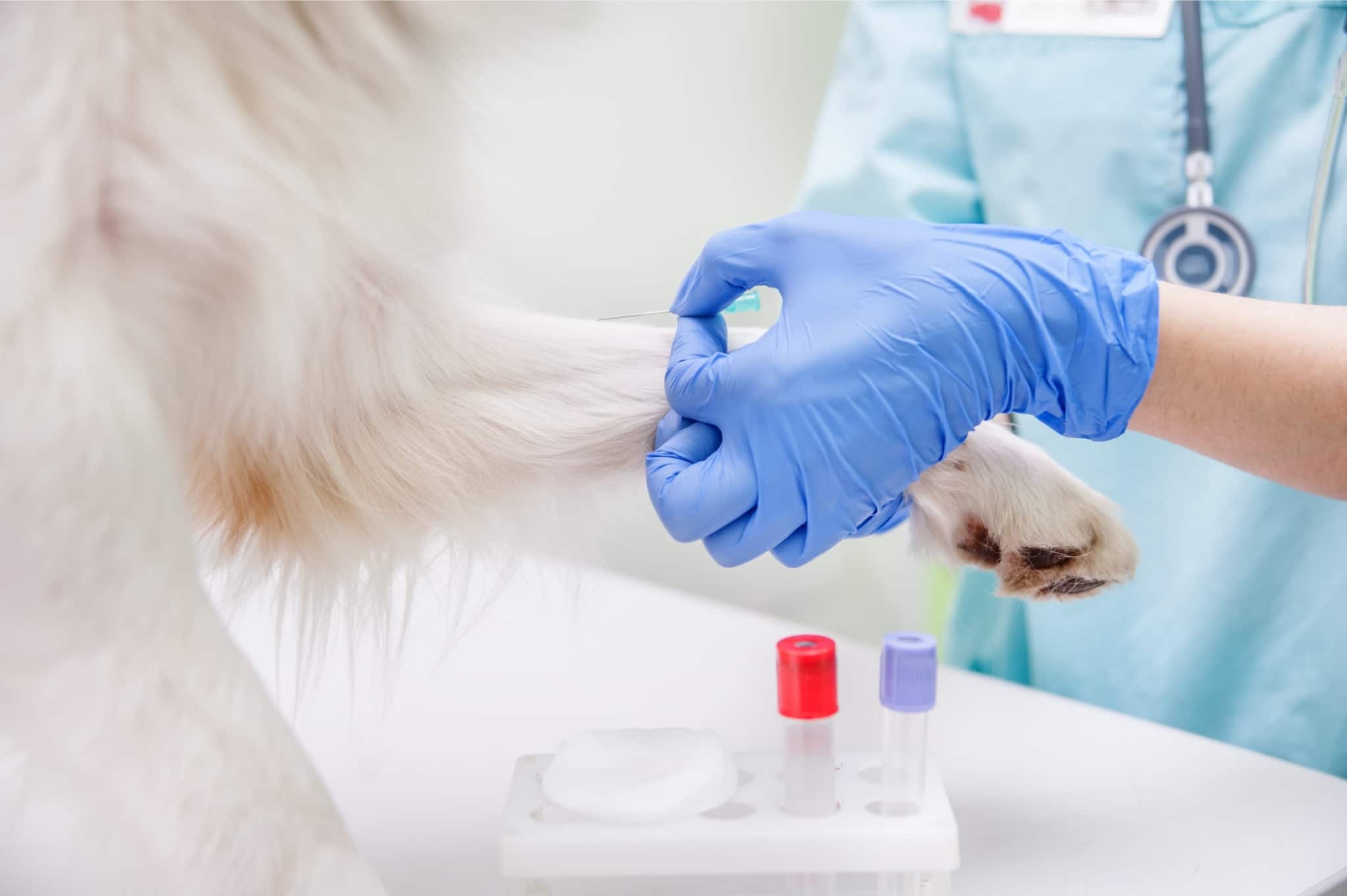
Treatment of alopecia in dogs
Let’s find out if alopecia in dogs is treated? Depending on the cause of alopecia and its severity, the prognosis can be different. Most cases of alopecia can be effectively treated if the problem is detected in time and the veterinarian’s recommendations are followed. How to treat focal hair loss in dogs will be described in more detail below.
We have already found out that this disease in dogs depends on the cause of its appearance, so it is important to establish an accurate diagnosis first.
Basic approaches to treatment

- Medical treatment:
– Anti-inflammatory drugs and antihistamines: Used to reduce inflammation and itching, especially if the cause of alopecia is allergy.
– Antibiotics and antifungals: Used for bacterial or fungal infections such as pyoderma or dermatophytosis.
– Hormonal drugs: If alopecia is associated with hormonal disorders (for example, hypothyroidism or Cushing’s syndrome), appropriate hormonal drugs are prescribed.
- Changing the diet and nutritional supplements:
– A diet rich in omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids: Helps to improve the condition of the skin and coat.
– Food supplements with biotin, B vitamins and zinc: Promote healthy coat growth and strengthening of the skin barrier.
- External treatment:
– Shampoos with antiseptic or antifungal properties: Used to clean the skin and reduce infections.
– Topical ointments or sprays: May include corticosteroids or other medications that reduce itching and inflammation.
- Immunotherapy:
– Used for allergies and autoimmune diseases that can cause alopecia. This may include hyposensitization (immune therapy) or the use of immunosuppressants.
- Treatment of parasites:
– Antiparasitic agents: Used in the presence of fleas, ticks or other ectoparasites that can cause hair loss.
- Treatment of endocrine diseases:
– If alopecia is associated with endocrine disorders, such as hypothyroidism, Cushing’s disease or sexual hormonal disorders, specific treatment should be carried out to normalize hormonal levels.
- Surgical treatment:
– In rare cases, when the cause of alopecia is a tumor or other neoplasm, surgical intervention may be necessary.
- Stress reduction and behavior correction:
– If alopecia is caused by stress or compulsive behavior, environmental changes, behavioral therapy, or sedatives may be helpful.
- Specialist assistance:
– Sometimes consultation of a veterinary dermatologist or endocrinologist is required for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
It is important to carry out a thorough diagnosis by a veterinarian to determine the cause of alopecia, as treatment largely depends on an accurate diagnosis.

Prevention of alopecia in dogs
To prevent alopecia in dogs, it is important to follow simple care rules:
– Regular visits to the veterinarian and groomer for timely diagnosis and treatment of diseases.
– Maintenance of cleanliness and hygiene, regular treatment against parasites.
– Balanced nutrition, including all necessary vitamins and minerals.
– Avoiding stress and providing comfortable housing conditions.
Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment of alopecia will help your dog quickly return to a normal life with a beautiful and healthy coat, and regular visits to a professional groomer at V.O.G DOG SALON dog beauty salons will guarantee your pet a healthy and well-groomed appearance throughout its life.









