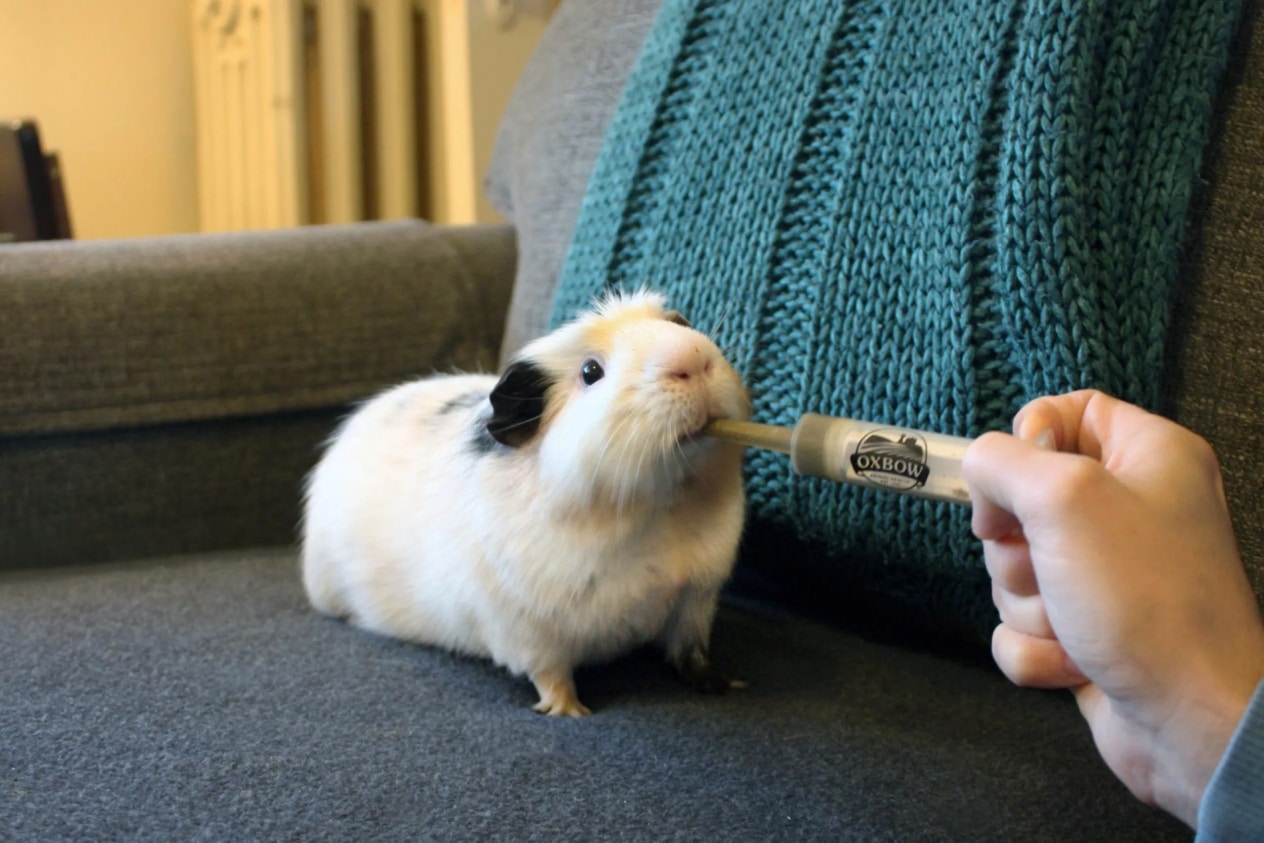
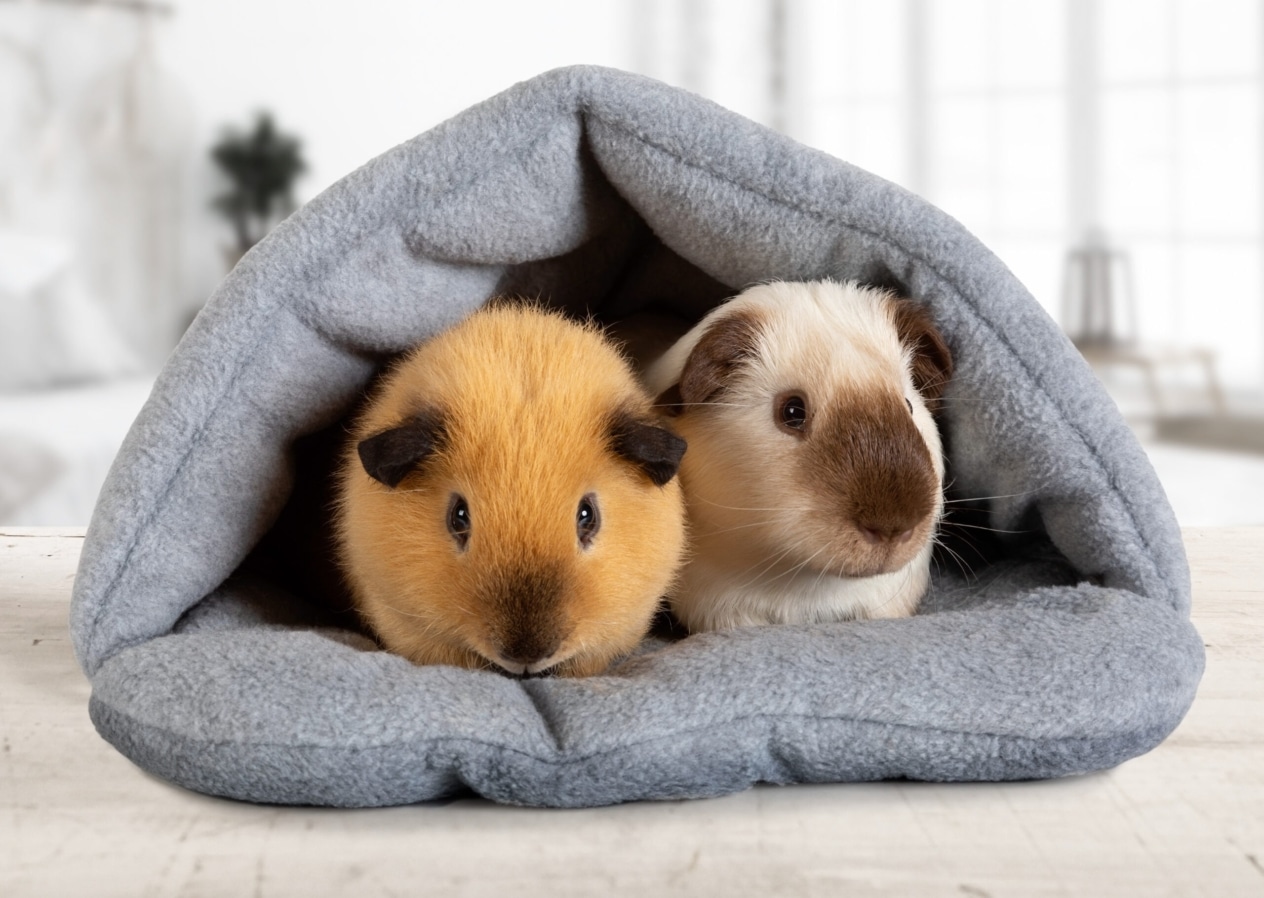
The guinea pig is a rather friendly pet that likes to spend time with the owner and brings him a lot of positive emotions. It is unpretentious, so its maintenance does not require special efforts and does not require appreciable financial costs. With proper nutrition and periodic veterinary examination, this animal can live for more than five years.
Maintaining a guinea pig’s good health starts with understanding its nutritional needs. Therefore, let’s talk about how to properly feed this pet, what should be in its diet and what products should be avoided, so as not to expose your pet to digestive disorders.
General information about nutrition
Guinea pigs have a high metabolic rate and require almost constant feeding. They are strictly herbivorous animals and should not be fed animal protein products.
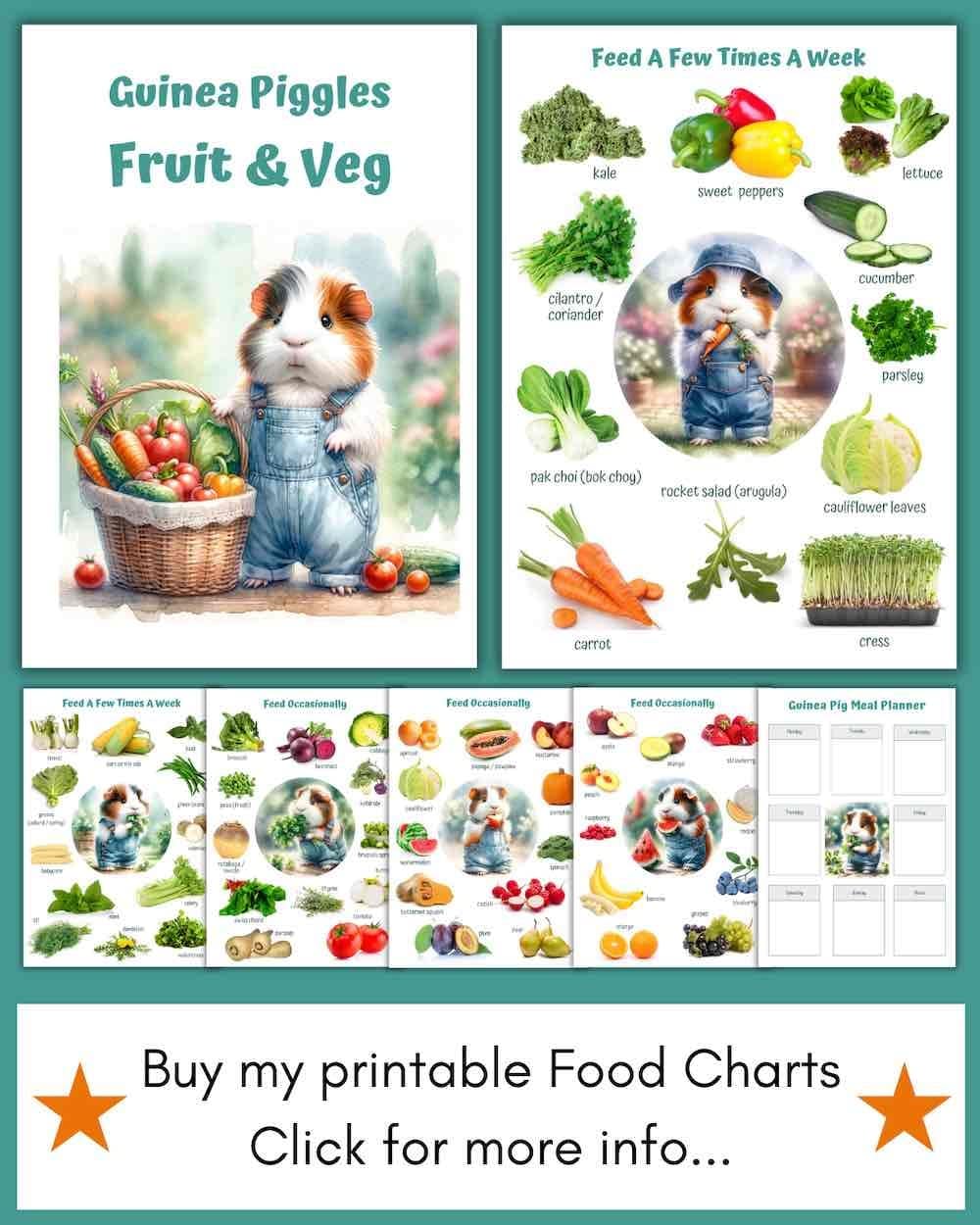
Grass hay, vegetables and herbs are the staples in this animal’s diet. Fruit is recommended very rarely, mainly as a treat, and should make up no more than 5% of the diet. It is very important to take care of the presence of vitamin C in the foods consumed by the guinea pig.
Sometimes you can use pelleted food that is designed for these pets. However, you need to choose only those mixtures that are certified and do not contain nuts and seeds. Veterinarians do not recommend them because of their high fat content, which can lead to overweight animals. It should be noted that such feeds should make up only a minimal part of the diet of guinea pigs, as their complete transfer to pellets can lead to digestive problems.
How to feed guinea pigs
Grass hay is the most important part of the guinea pig diet, so they should have constant access to it in the feeder. These animals love hay made from a variety of meadow grasses and from timothy grass, which is specially grown as food for rabbits, guinea pigs and other herbivorous rodents. Hay should be dried in advance, 6-7 weeks in advance, and varied, as each grass has a unique chemical composition and provides different nutrients. For example, clover and alfalfa hay is best used only for young or pregnant animals as it is high in calcium and calories. During the warmer months of the year, guinea pigs can eat fresh grasses such as yarrow, clover, dandelion, and wheatgrass.
Unlimited access to hay prevents dental and gastrointestinal diseases common among these pets. The fact is that the structure of grasses is abrasive, and this helps to sharpen the constantly growing teeth of the guinea pig. Without such grinding, the teeth may grow back too much, and this will lead to problems with nutrition and general health of the animal.
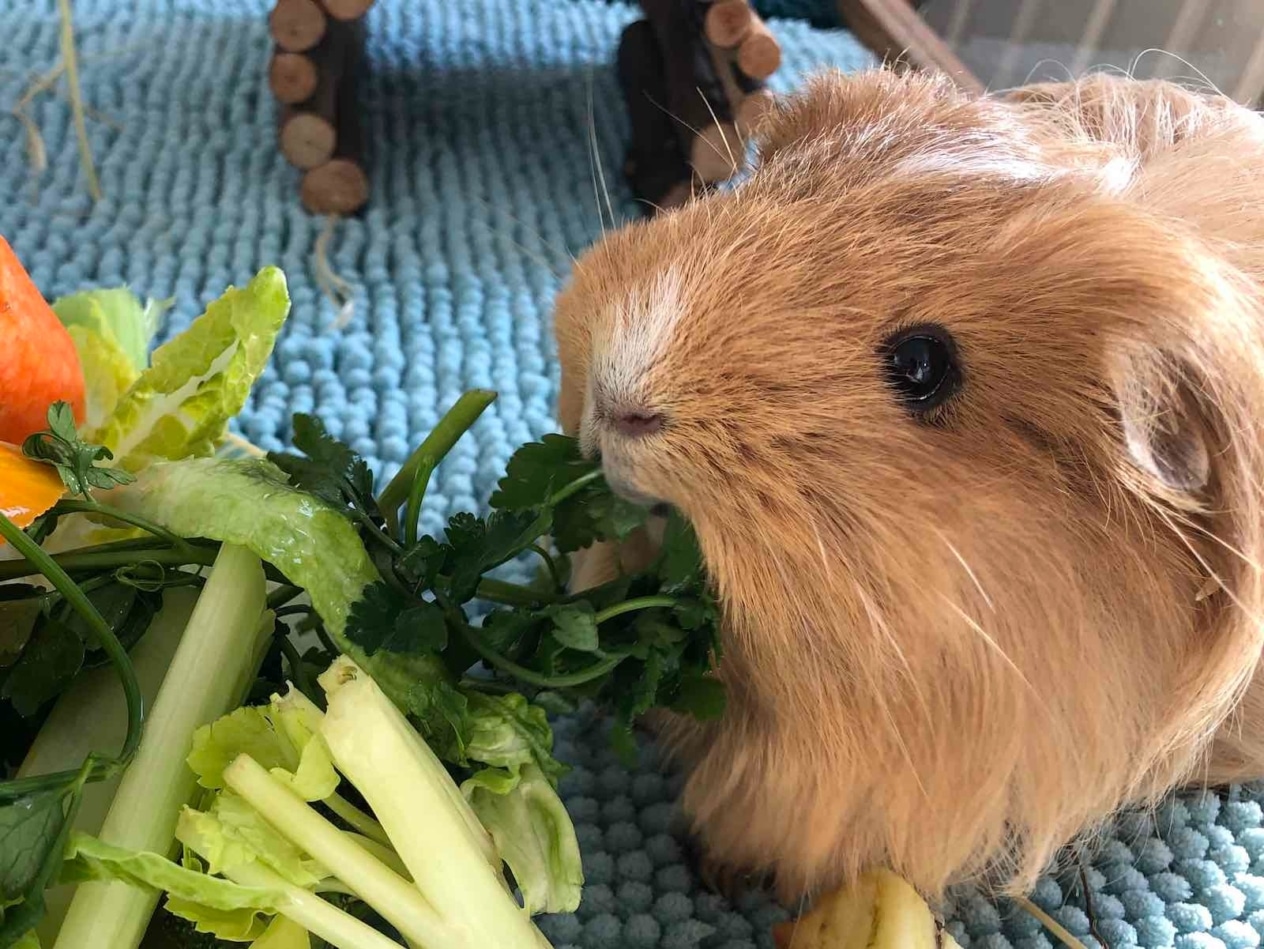
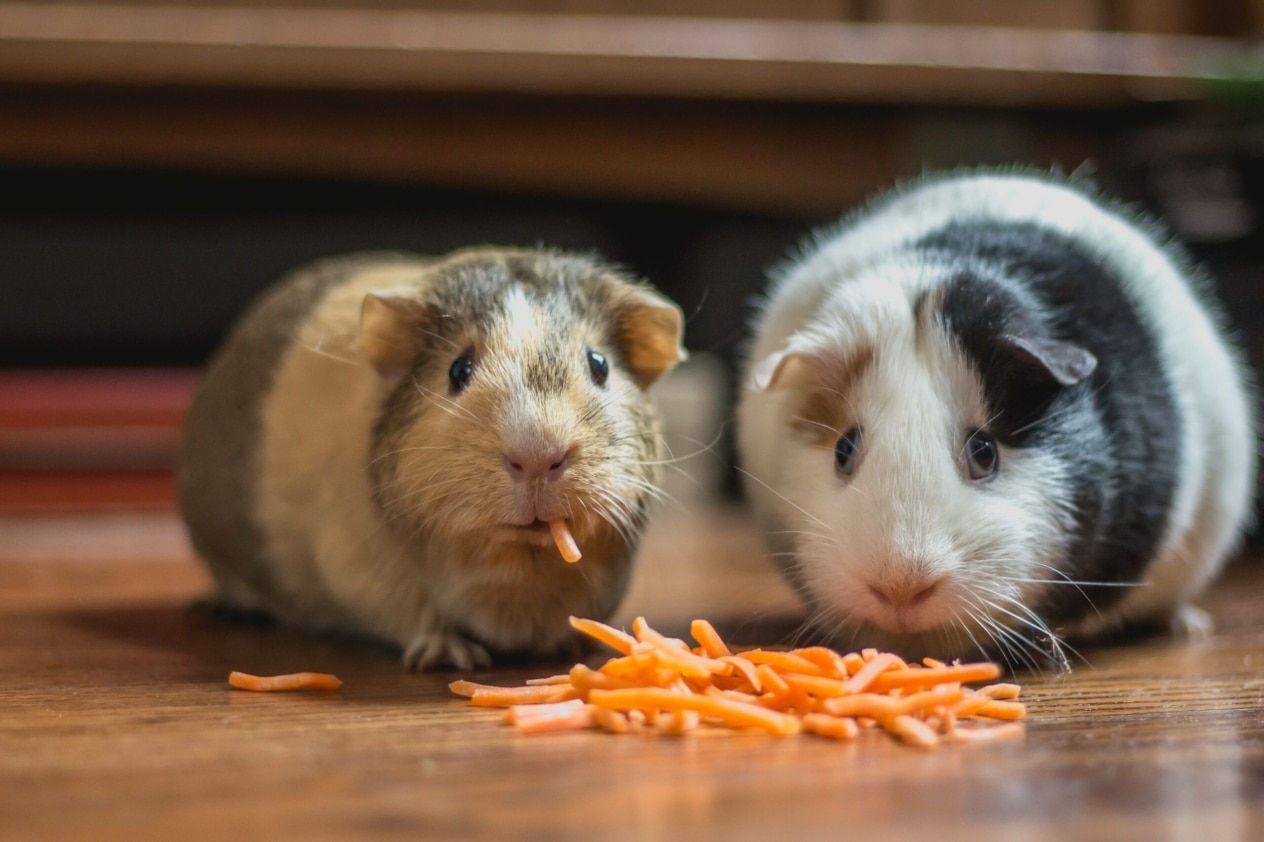


Vegetables and greens are another important part of a guinea pig’s diet. Veterinarians advise introducing one new vegetable at a time and monitoring the pet’s gastrointestinal response to it. After the pet is familiarized with all the vegetables, you can offer her half to one cup of vegetable mixture of 2-3 different vegetables daily. Greens (dill, parsley, leaf lettuce, spinach) and vegetables (carrots, cucumbers, peppers, celery) should be a daily addition to the diet.
Pelleted food can be offered to guinea pigs in limited quantities – usually 1-2 tablespoons per day. It is a specially formulated food that provides a balanced diet just for these rodents, because it contains nutrients, vitamins and minerals. The food has the form of granules, which helps to avoid selective consumption of products, because it is the granules that guarantee an even supply of all the necessary components. In addition, the hard texture of the granules helps to properly grind the pig’s teeth, which is important for the health of its oral cavity.
Fruit should only be given to these pets 1-2 times a week because of the high amount of sugar in them. These are “empty calories” that have little nutritional value for guinea pigs, and can lead to obesity and problems with excessive flatulence (gas). Periodically, guinea pigs can be given fruits such as pineapple, melon, kiwi, apple and berries.
Vitamin C is a food supplement that should definitely be present in the diet of guinea pigs. This is because guinea pigs, like humans, are unable to produce this vitamin on their own because they lack the enzyme needed to synthesize ascorbic acid. Low levels of this vitamin leads to the development of scurvy, which in these animals is manifested by bleeding gums, joint pain, hair problems and decreased immunity. Therefore, these favorites need to either consume foods rich in vitamin C, such as kiwi, peppers, parsley, or get it in the form of tablets, which should be crushed and mixed with food. The daily requirement of guinea pigs for this vitamin is 20 mg/kg and increases to 60 mg/kg during illness, pregnancy and lactation. In any case, such prescriptions should be discussed with a veterinarian.
Water shouldalways be near the guinea pig, because its lack in the animal’s body can lead to dehydration and other health problems. For this purpose, it is better to use a hanging drinking bottle with a metal nipple, which is attached to the side of the cage. It is important to check regularly that the drinker is working well, that there is water in it, and that the bottle is clean and filled daily with fresh filtered water.
What foods should be avoided in a guinea pig’s diet
Never feed nuts, seeds and dried fruits to yourguinea pig. They are not recommended because of their high fat and sugar content, as they can lead to obesity problems and stomach upset.
Meat and animal products are strictly forbidden to guinea pigs. They are herbivorous animals, so their digestive system is not designed to digest meat. If guinea pigs eat animal products, they can develop serious health problems, including severe food poisoning.
Feeding starchy foods such as potatoes, beans (in large quantities), peas and bread toguinea pigs is also not recommended. These can cause intestinal bloating and stomach problems.
Dairy products from cow’s and goat’s milk are prohibited in the diet of adult guinea pigs because their bodies no longer produce the special enzyme lactase, which breaks down milk sugar (lactose). Therefore, consumption of such products can lead to digestive problems such as diarrhea, bloating and stomach pain.
Avoid or very limited consumption of cruciferous foods such as white cabbage, Chinese cabbage, cauliflower, broccoli by pigs. They can cause gas and bloating in these animals.
It is not necessary to treat guinea pigs with food from the owner’s table, no matter how tasty it may seem. Very often these animals are treated by a veterinarian after such dishes, because most of them contain sugar, salt and other spices that are harmful to the body of pigs.
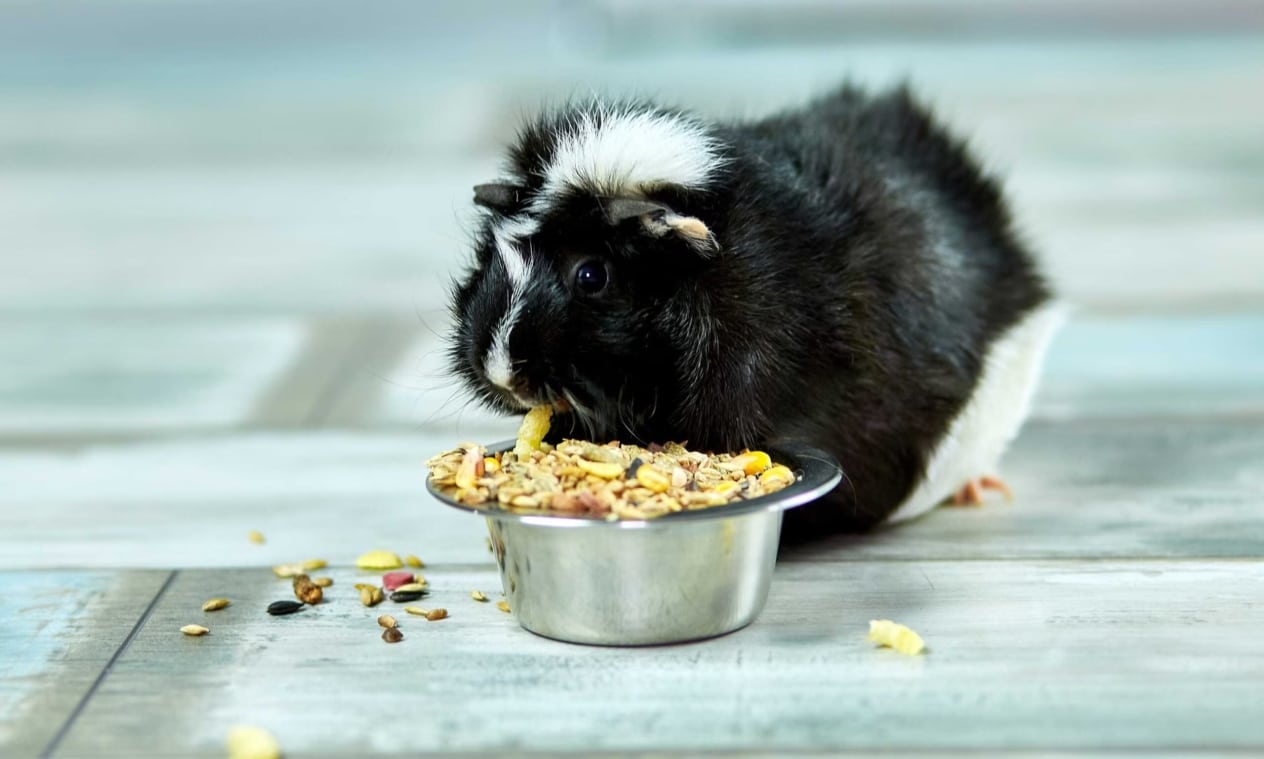

So, by nature, guinea pigs are strictly herbivorous. They need fiber-rich food and frequent feeding in small portions. By following all of the above recommendations, you are sure to provide your pet with a healthy and carefree life.